How to read currency pairs
One of the fundamental concepts in forex trading is the concept of currency pairs. A currency pair consists of two currencies being traded against each other - the base currency and the quote currency. For example, in the currency pair EUR/USD, the EUR is the base currency, and the USD is the quote currency. Understanding how to read currency pairs is of utmost importance for anyone venturing into forex trading as it forms the basis of all forex transactions. A solid understanding of currency pairs will help you make informed decisions and significantly increase your chances of success in the forex market.
What are currency pairs?
Currency pairs are the fundamental units of the forex market. A currency pair consists of two different currencies being quoted against each other. The first currency in the pair is called the 'base currency,' and the second currency is called the 'quote currency.'
For example, in the currency pair EUR/USD, the EUR is the base currency, and the USD is the quote currency. This means that the currency pair's price represents how much the quote currency is needed to purchase one unit of the base currency. So, if the EUR/USD is trading at 1.2000, 1 Euro (the base currency) is equivalent to 1.20 US Dollars (the quote currency).
There are many different currency pairs available for trading in the forex market. They are typically categorized into three main groups: Major Pairs, Minor Pairs, and Exotic Pairs. Major Pairs are the most traded currency pairs, including the world's most liquid and widely used currencies. Understanding the difference between base and quote currencies and how they interact is crucial for trading successfully in the forex market.
The major currency pairs
The major currency pairs are the most traded and liquid currency pairs in the forex market. These pairs consist of the world's most powerful and stable currencies. There are seven major currency pairs, and they all include the US dollar (USD):
EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar)
USD/JPY (US Dollar/Japanese Yen)
GBP/USD (British Pound/US Dollar)
USD/CHF (US Dollar/Swiss Franc)
AUD/USD (Australian Dollar/US Dollar)
USD/CAD (US Dollar/Canadian Dollar)
NZD/USD (New Zealand Dollar/US Dollar)
These pairs are the most popular among traders because they offer the lowest spreads and highest liquidity, meaning it is easier to enter and exit positions. Also, because of their popularity, these pairs tend to have more market analysis available, making it easier for traders to make informed decisions.
The major currency pairs are crucial in the global forex market. They represent the world's largest economies and are used as the standard currency for commodities such as oil and gold. Trading the major currency pairs is often recommended for beginners due to their high liquidity and lower volatility than minor and exotic pairs.
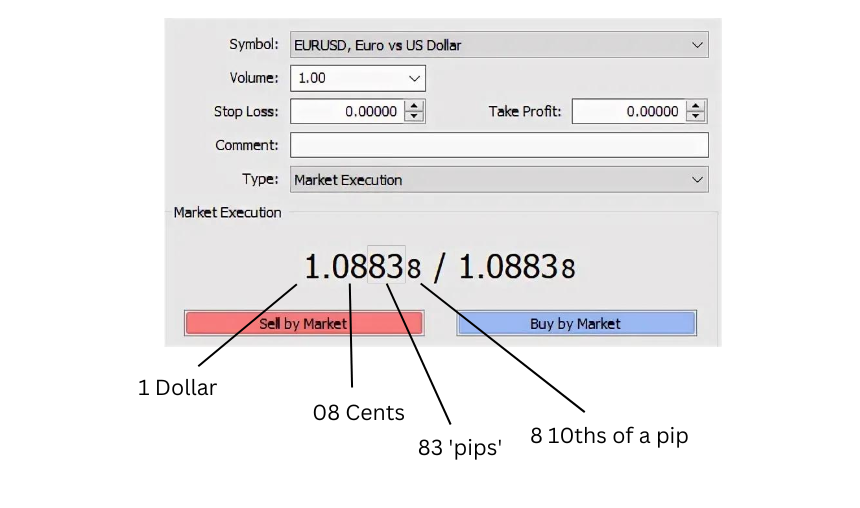
Reading currency pairs
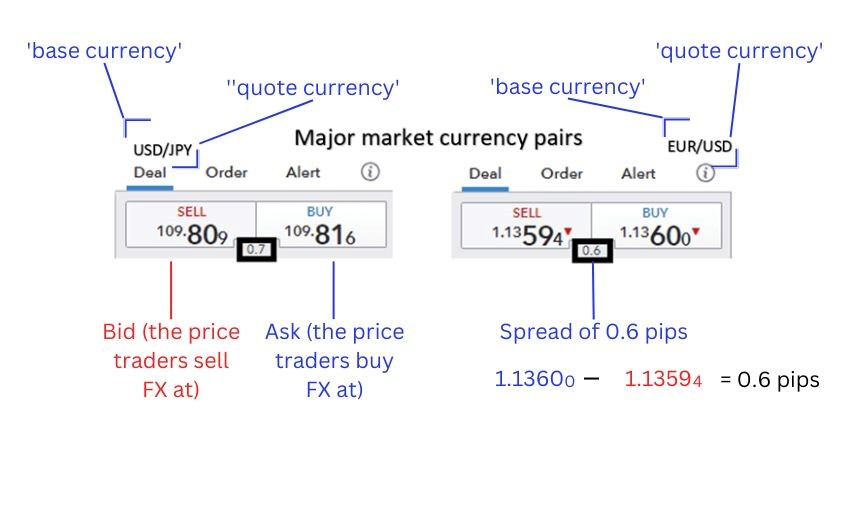
Understanding the currency pair notation is crucial for trading in the forex market. The notation consists of the base currency followed by the quote currency. For example, in the currency pair EUR/USD, EUR is the base currency, and USD is the quote currency.
The price of a currency pair is quoted using the bid price and the ask price. The bid price is the price at which you can sell the base currency, and the asking price is the price at which you can buy the base currency. The difference between the bid and ask price is known as the spread.
For example, if the EUR/USD is quoted with a bid of 1.1359 and an ask of 1.1360, you can sell one Euro for 1.1359 US Dollars or buy one Euro for 1.1360 US Dollars. The spread in this case would be 60 pips (a pip is the smallest price movement in the forex market and is equal to 0.0001).
Understanding the bid and ask prices and how to read them is crucial for executing trades and managing risk in the forex market.
Factors influencing currency pairs
Various factors influence the prices of currency pairs in the forex market. These can be broadly categorized into three groups: economic factors, political factors, and market sentiment.
Economic factors are indicators that reflect the economic health of a country or region. Key economic indicators include GDP growth, employment data, inflation rates, interest rates, and trade balances. For example, a rise in interest rates in a country typically strengthens its currency as it offers better returns to investors.
Political factors include events and decisions that affect a country's political stability or policies. Examples include elections, government policies, geopolitical tensions, and political instability. For example, political instability in a country often leads to a weakening of its currency.
Market sentiment refers to the overall mood of the market participants. It can be influenced by news events, reports, and other market data. For example, positive news about a country's economy often leads to a strengthening of its currency.
Traders need to be aware of these factors and how they influence currency pairs, as they can lead to sudden and significant movements in the forex market.
How to analyze currency pairs
Analyzing currency pairs involves evaluating the various factors that can influence their price movements. There are two main methods of analysis used by traders: fundamental analysis and technical analysis.
Fundamental analysis involves analyzing the economic, political, and social factors that influence the prices of currencies. Traders use economic indicators, political events, and market sentiment to predict the future movements of currency pairs. For example, a strong GDP growth rate in a country may strengthen its currency.
Technical analysis involves analyzing historical price data and using technical indicators to predict future price movements. Traders use charts, patterns, and indicators such as moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), and Fibonacci retracement levels to make predictions about the future movements of currency pairs.
Both fundamental and technical analysis are essential for trading in the forex market. While fundamental analysis helps traders understand the underlying reasons for price movements, technical analysis helps them identify trends and predict future movements. It is recommended for traders to use a combination of both methods to make more informed trading decisions.
Trading strategies
Developing a well-thought-out trading strategy is crucial for success in the forex market. A trading strategy is a set of rules and guidelines that a trader follows when entering or exiting a trade. There are various trading strategies popular among forex traders, and they usually fall into one of the following categories:
Trend following: This strategy involves identifying the direction of the market trend and placing trades that align with that trend. Traders use technical indicators such as moving averages and the relative strength index (RSI) to identify the trend direction.
Range trading: This strategy involves identifying the support and resistance levels of a currency pair and placing trades within that range. Traders use technical indicators such as the stochastic oscillator and the average true range (ATR) to identify the support and resistance levels.
Breakout trading: This strategy involves identifying critical support and resistance levels and placing trades when the price breaks through these levels. Traders use technical indicators such as the moving average convergence divergence (MACD) and the RSI to identify breakout levels.
Risk management and currency pairs
Risk management is a crucial aspect of forex trading that beginners often overlook. It involves identifying, assessing, and managing the risks of trading currency pairs in the forex market. Proper risk management can help traders minimize losses and maximize profits.
Set stop loss and take profit levels: Stop loss is an order placed to sell a security when it reaches a specific price, while take profit is an order placed to sell a security when it reaches a certain profit level. Setting stop loss and take profit levels helps traders manage risk and lock in profits.
Use proper leverage: Leverage allows traders to control a large position with a small amount of capital. However, it also increases the risk of losses. It is important to use leverage wisely and not to over-leverage your account.
Diversify your portfolio: Do not put all your eggs in one basket. Diversify your portfolio by trading different currency pairs or other asset classes.
Monitor market news: Economic and political events can significantly impact currency pairs. Staying informed about market news and adjusting your trading strategy accordingly is important.
Keep emotions in check: Trading is a psychological game. It is essential to keep your emotions in check and not let fear or greed dictate your trading decisions.
By implementing proper risk management techniques, traders can minimize their losses and maximize their profits when trading currency pairs in the forex market.
Conclusion
Reading currency pairs effectively is paramount for success in the forex market. As we have seen, understanding the currency pair notation, including the base and quote currencies and the bid and ask prices, is fundamental. Being cognizant of the various factors influencing currency pairs is essential for making informed trading decisions. Crafting a well-thought-out trading strategy encompassing fundamental and technical analysis is key to successfully navigating the forex market. Utilizing proper risk management techniques is crucial to safeguard your investments and maximize profits.



