Know all about forex hedging
Forex hedging is more than just a strategy; it's a shield against the inherent volatility of the forex market. Understanding hedging is paramount for traders and businesses alike, as it offers a means to safeguard investments and mitigate potential losses. Whether you are an individual trader aiming to protect your capital or a multinational corporation engaged in international trade, grasping the fundamentals of hedging can be the key to navigating the unpredictable terrain of foreign exchange.
What is forex hedging?
Forex hedging is a strategic risk management technique employed by traders and businesses engaged in currency markets. At its core, hedging involves taking deliberate actions to offset or minimize the potential losses resulting from adverse price movements in the foreign exchange market. It is a proactive approach that seeks to safeguard financial interests against unfavourable currency fluctuations.
In the world of currency trading, risk is an ever-present companion. Exchange rates are subject to fluctuation due to various factors, including economic events, geopolitical developments, and market sentiment. Forex hedging is designed to mitigate this risk by creating a counterbalancing position or employing financial instruments that move inversely to the primary exposure. By doing so, traders and businesses aim to neutralize the impact of adverse exchange rate movements, ensuring a more predictable outcome for their financial endeavours.
The objectives of hedging in the forex market are multifaceted. Firstly, it seeks to protect investments from potential losses, ensuring capital preservation. Secondly, hedging allows traders and businesses to maintain a stable financial position in the face of volatile currency markets. Additionally, it can provide the confidence needed to engage in international trade, knowing that currency risks are effectively managed. Lastly, hedging strategies can enhance financial planning and budgeting, contributing to more accurate forecasting and decision-making processes.
FX hedgings strategies
Forex hedging offers a diverse range of strategies, each tailored to specific risk management needs. Here are three commonly used approaches:
Forward contracts: A forward contract is an agreement between two parties to exchange a specified amount of one currency for another at a predetermined future date and exchange rate. This strategy provides certainty in currency exchange rates, making it a valuable tool for businesses involved in international trade.
Options: Currency options give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency pair at a predetermined rate (the strike price) within a specified time frame. Options offer flexibility and can be used to protect against unfavourable exchange rate movements while allowing the opportunity to benefit from favourable moves.
Currency swaps: A currency swap involves the exchange of principal and interest payments in one currency for equivalent amounts in another currency. This strategy is often used by multinational corporations to manage long-term currency exposure, such as debt or investments.
Pros and Cons of each strategy
Forward contracts: Pros include rate certainty and protection against adverse exchange rate movements. However, they lack flexibility as the exchange rate is fixed, potentially causing missed profit opportunities if rates move favourably.
Options: Pros include flexibility and limited downside risk (premium paid). However, options come with a cost (premium), which can erode profits if the market behaves favourably. They also require a good understanding of option pricing.
Currency swaps: Pros include flexibility and the ability to manage long-term exposures. However, they may involve complex documentation and may not be suitable for short-term hedging needs.
Examples of how each strategy can be used effectively
Imagine a U.S. company exporting goods to Europe and expecting payment in euros in six months. To protect against a potential depreciation of the euro, the company could:
By entering into a forward contract to sell euros at a predetermined rate, the company ensures it will receive a known amount in dollars regardless of the exchange rate at the time of payment.
Alternatively, the company could buy a currency option that allows it to sell euros at a specific rate if the euro weakens. This provides protection while allowing participation in euro gains.
For long-term exposure, such as financing a European subsidiary, the company might use currency swaps to manage interest rates and currency risk over an extended period.
Hedging meaning in forex
In the context of the forex market, hedging refers to a strategic practice aimed at minimizing or offsetting the risks associated with currency exchange rate fluctuations. It's a proactive approach where traders and businesses take deliberate actions to protect their positions and investments from adverse currency movements. Hedging is not about speculative gains but rather about safeguarding the value of assets and ensuring financial stability.
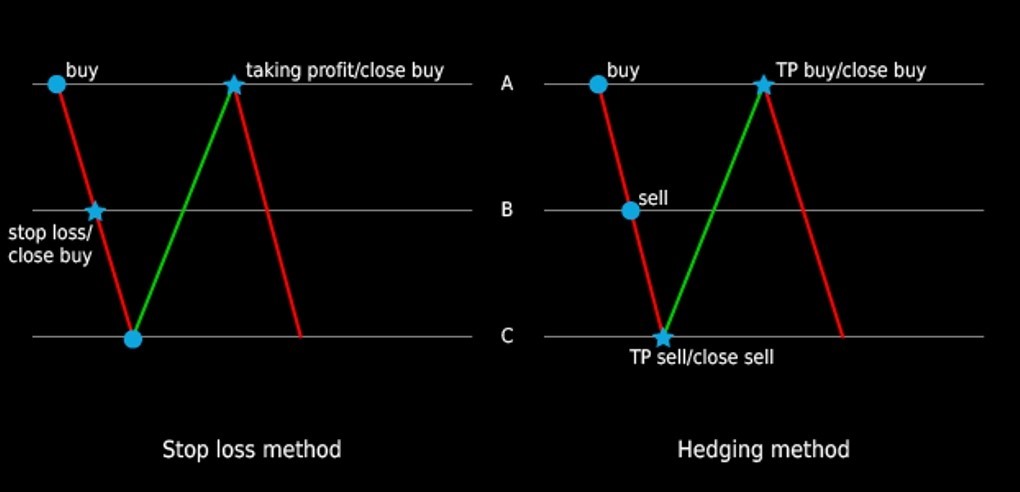
Hedging in forex involves opening positions that are opposite to existing or anticipated market positions. For instance, if a trader expects the value of a particular currency pair to decline, they may enter a hedging position that profits from this expected decline. This way, if their primary position incurs losses due to adverse market movements, the hedging position can potentially offset those losses.
The primary role of hedging in the forex market is risk reduction. By using various hedging strategies, traders and businesses can create a protective shield around their financial interests. Hedging is akin to having an insurance policy against unfavourable market conditions. It provides a level of predictability in an otherwise volatile environment, ensuring that losses are limited or controlled.
Hedging foreign exchange risk
Foreign exchange risk, often referred to as currency risk, is an inherent challenge in international business and forex trading. It arises from the potential fluctuations in exchange rates between two or more currencies, impacting the value of financial assets, liabilities, or transactions. This risk can lead to unpredictable gains or losses when dealing with foreign currencies.
Forex hedging plays a pivotal role in managing and minimizing foreign exchange risk. By employing hedging strategies, individuals and businesses can effectively shield themselves against adverse currency movements. For instance, if a company imports goods from abroad and must pay in a foreign currency at a future date, it can use hedging instruments like forward contracts to lock in the exchange rate, ensuring the cost remains predictable. Conversely, if a company expects to receive payments in foreign currency, options can be utilized to safeguard against unfavourable currency depreciation.
Numerous multinational corporations employ forex hedging to protect their financial interests. For instance, a U.S.-based tech company with global operations may use hedging to mitigate the risk of currency fluctuations impacting its international revenues. Similarly, an airline that purchases aircraft from a European manufacturer may enter into currency swaps to manage its exposure to exchange rate shifts. These real-world examples illustrate how forex hedging is an indispensable tool for companies engaged in cross-border transactions, ensuring stability and predictability in a volatile forex landscape.
Benefits of forex hedging
Incorporating hedging strategies into your forex trading or business operations offers a multitude of advantages:
Risk mitigation: The primary benefit of hedging is the ability to reduce or control potential losses caused by adverse currency movements. This risk mitigation provides peace of mind and financial security.
Predictable cash flows: For businesses engaged in international trade, forex hedging ensures that cash flows remain predictable, allowing for more accurate budgeting and financial planning.
Capital preservation: Traders can protect their capital from significant losses, enabling them to stay in the market and continue trading even during volatile periods.
Increased confidence: Hedging strategies provide a sense of confidence and stability, which can be especially crucial in the face of unpredictable forex market conditions.
Volatility is an inherent characteristic of the currency market, making it susceptible to sudden and significant price swings. Forex hedging acts as a shield against this volatility. Traders can enter hedging positions that offset potential losses from adverse market movements. Businesses, on the other hand, can secure exchange rates for future transactions, shielding themselves from unfavorable currency fluctuations. In doing so, both traders and businesses are better equipped to weather market turbulence and navigate the forex landscape with confidence.
Risks and Challenges
While forex hedging offers numerous benefits, it is essential to acknowledge and understand the potential drawbacks and challenges:
Costs: Hedging strategies often involve fees, premiums, or spreads, which can eat into profits. It's crucial to weigh the cost of hedging against the potential benefits.
Over-hedging: Overzealous hedging can lead to missed profit opportunities. Striking the right balance between protection and profit generation is a challenge.
Market timing: Accurately predicting market movements is challenging. Hedging too early or too late can result in suboptimal outcomes.
Complexity: Some hedging instruments, such as options and derivatives, can be complex. A lack of understanding may lead to errors or losses.
To manage the risks and challenges associated with forex hedging effectively, consider the following strategies:
Cost-benefit analysis: Always evaluate the costs of hedging against potential losses. Choose the most cost-effective hedging strategy that aligns with your risk tolerance and trading goals.
Diversification: Diversify your portfolio to reduce reliance on a single hedging strategy. This spreads risk and can enhance long-term performance.
Education: Invest time in learning about the specific hedging instruments you plan to use. Understand their mechanics, advantages, and limitations.
Regular monitoring: Continuously monitor your hedging positions and adjust them as market conditions evolve. Avoid overcommitting to a single strategy or locking yourself into a long-term position without flexibility.
Professional advice: Seek guidance from experienced forex professionals or financial advisors, especially when dealing with complex hedging instruments.
Conclusion
Forex hedging is not merely a trading strategy; it's a shield against the inherent volatility of the forex market. It offers risk mitigation, capital preservation, and financial stability. Understanding and utilizing forex hedging is a vital aspect of responsible trading and international business operations. It enables traders and businesses to safeguard their financial interests and navigate the complex landscape of currency markets with confidence.
Hedging doesn't eliminate risk entirely, but it mitigates the impact of adverse currency fluctuations. It's particularly valuable for businesses engaged in international trade, as it allows them to plan and budget with greater certainty. By understanding the dynamics of hedging, market participants can effectively manage risk, enhance financial stability, and make informed decisions in the ever-evolving world of forex trading.



